September 06, 2024
Viruses and Bacteria: Understanding the Key Differences
We often hear terms like viruses and bacteria when we think of fever. While they belong to microorganisms they are fundamentally different in their nature and behavior. Our journey into understanding viruses and bacteria is not just an academic exercise but a practical necessity. It helps us understand why certain infections require specific treatments and why some preventive measures work against one but not the other. For instance, the antibiotics that are so effective against bacterial infections are useless against viruses, which require a different set of strategies for treatment and prevention.
In this blog, we will learn a detailed guide about viruses and bacteria, and how they influence our health. Moreover, you'll have a clearer picture of how to better protect yourself.
What Are Viruses?
Viruses are tiny infectious agents that are fundamentally different from living organisms. Unlike bacteria, viruses lack cellular structures and cannot perform life processes on their own. They are composed of genetic material (either DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat. An exterior lipid coating is also present in some viruses. Because they lack the machinery for metabolism and reproduction, viruses must hijack the cells of a host organism to replicate and spread.
How Viruses Operate:
- Infection: A virus attaches to a host cell using specific proteins on its surface. This attachment is important for the virus to enter the cell.
- Replication: Once inside, the virus takes over the cell’s machinery to replicate its genetic material and produce new virus particles.
- Release: The newly formed viruses are released from the host cell, often destroying it in the process, and go on to infect other cells.
Viruses can cause a range of diseases, from the common cold to severe illnesses like HIV/AIDS and COVID-19. Antiviral medications and vaccines are the primary methods of treatment and prevention, as antibiotics are ineffective against viruses.
What Are Bacteria?
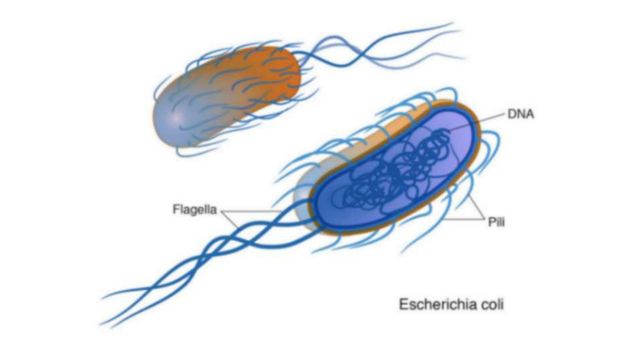
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that have a more complex structure compared to viruses. They are living entities capable of independent life processes. Bacteria have a cell wall, a cell membrane, and genetic material in the form of DNA. They can survive and reproduce on their own, and they play various roles in both health and disease.
How Bacteria Operate:
- Reproduction: Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, where a single bacterial cell divides into two identical cells.
- Metabolism: Bacteria can metabolize nutrients and produce energy independently.
- Interaction with Hosts: While many bacteria are beneficial, some can cause diseases such as tuberculosis or strep throat.
Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics, which target specific bacterial functions. Vaccines are also available for some bacterial diseases, helping to prevent infections.
Key Differences Between Viruses and Bacteria
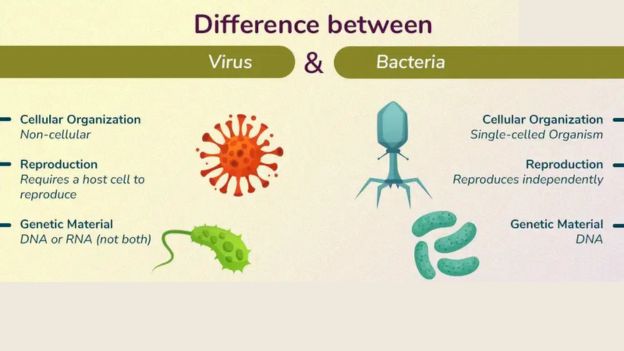
Understanding the distinctions between viruses and bacteria is essential for effective treatment and prevention. Here’s an in-depth look at the primary differences:
1. Structure:
- Viruses: Compared to bacteria, viruses are far simpler. Their composition consists of genetic material (DNA or RNA) covered in a protein coat, occasionally accompanied by an extra lipid envelope. They are incapable of carrying out life functions on their own since they lack cellular structures.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled organisms with a complex structure. They have a cell wall, cell membrane, and internal machinery for metabolism and reproduction. Bacteria possess DNA organized into a single circular chromosome and sometimes additional plasmids.
2. Reproduction:
- Viruses: Viruses reproduce only inside host cells. They hijack the host’s cellular machinery to replicate and assemble new virus particles, which are then released to infect other cells.
- Bacteria: Bacteria reproduce independently through binary fission. They can grow and divide without needing a host organism.
3. Living or Non-Living:
- Viruses: Viruses are often considered non-living because they cannot carry out life processes on their own. They rely entirely on host cells for replication and survival.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are living organisms. They can perform all necessary life functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction, independently of a host.
4. Treatment:
- Viruses: Viral infections are treated with antiviral medications or vaccines. Antiviral drugs can inhibit viral replication, while vaccines can prevent infections by stimulating the immune system.
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics, which target specific bacterial processes or structures. Vaccines can also be used to prevent bacterial diseases.
5. Size:
- Viruses: Viruses are generally much smaller than bacteria, often measured in nanometers (nm). This small size allows them to infiltrate host cells but makes them difficult to see with standard microscopes.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are larger than viruses, typically measured in micrometers (µm). They are visible under a light microscope and can be directly observed and identified.
6. Genetic Material:
- Viruses: Viruses can contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material. This variability affects how viruses replicate and interact with host cells.
- Bacteria: Bacteria have DNA organized into a single circular chromosome, along with additional plasmids that can carry extra genes. This genetic organization supports their ability to adapt and evolve.
Why Does It Matters?
Before beginning the treatment process or even thinking about preventive strategies, it is essential to recognize the differences between viruses and bacteria. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments, such as using antibiotics for viral infections, which not only fails to help but can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
For accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, it's important to consult healthcare professionals who can provide the right tests and interventions.
PrepMed offers comprehensive medical resources and tools to help you understand and manage various health conditions. With accurate information and expert guidance, you can make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Join PrepMed Today!
If you're an aspiring doctor and seeking reliable information and resources about viruses, bacteria, and overall health management, visit our official website PrepMed. Our platform provides up-to-date medical knowledge, tools, and expert advice to support your health journey. Explore our resources today and take proactive steps towards a healthier future!
Understanding viruses and bacteria not only enhances your knowledge but also helps you to make better health decisions.
Stay informed, stay healthy, and let PrepMed be your partner in health management.
Follow Us - on Facebook /Instagram/ YouTube






